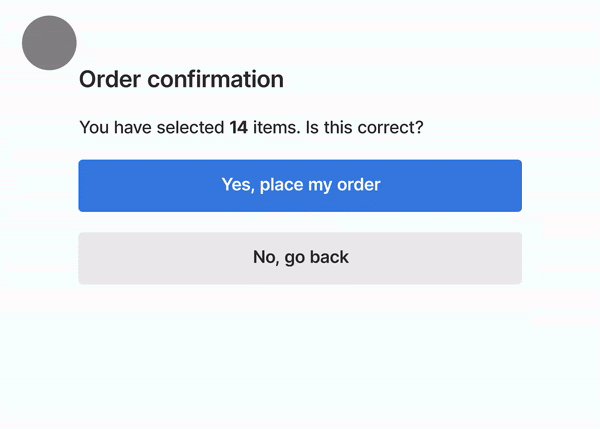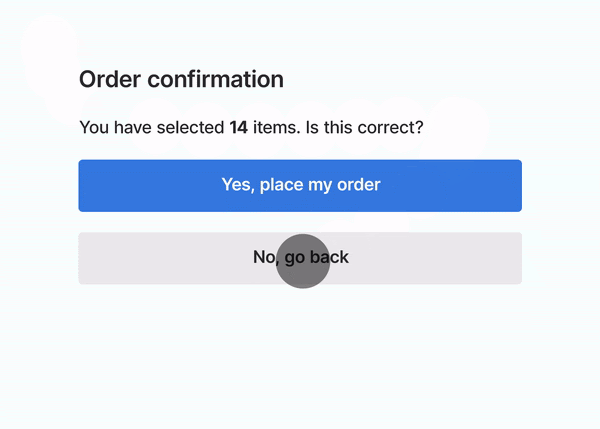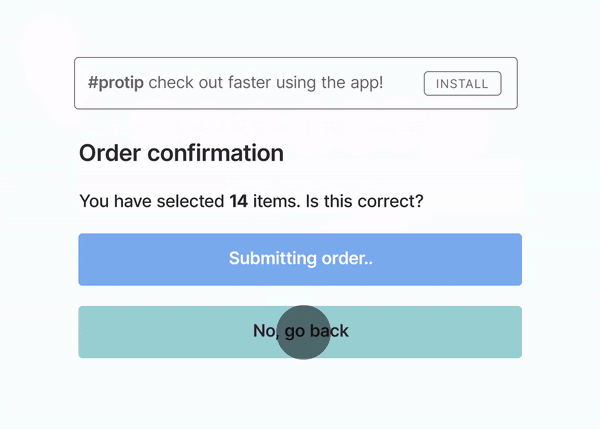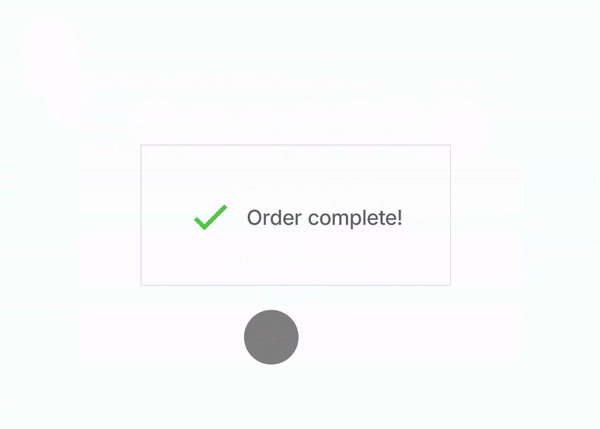
The average person today will digest more information than at any other point in history. Through the internet, music, TV and plain old fashioned print media, they’ll encounter around 100,000 words. Or about 2.5 novels. In total, they’ll process the equivalent of 34 gigabytes of information every day; 5 times more than 30 years ago.
These figures could give the impression that society in 2015 is more educated. With Google, Siri, and blogs like this just a few clicks away, we can encounter a wealth of information, learning whatever we feel like, whenever we feel like. Want to know tomorrow’s weather? Who was King of France in 1390? How tall Noel Edmonds is? There’s nothing stopping you.
However, have you ever thought that a lot of the information you encounter, process and learn might be wrong? Google has, and they’re wanting to rectify this.
For just under a year, Google has been developing their Knowledge Vault, a huge store of information taken from all across human history. Knowledge Vault is an ever expanding database that autonomously collects data from around the internet. This information is then cross referenced with similar or corresponding information in order to sift facts from falsities.
Google’s existing Knowledge Graph works in a similar way, albeit on a smaller scale. However, rather than compiling information from the whole of the internet, the Knowledge Graph uses “trusted” sources like Wikipedia and Freebase to offer a collection of related and relevant information on a given search term. For example, if I search “Noel Edmonds”, Knowledge Graph provides a collection of useful and unimaginably interesting facts on the man himself, as visible below.

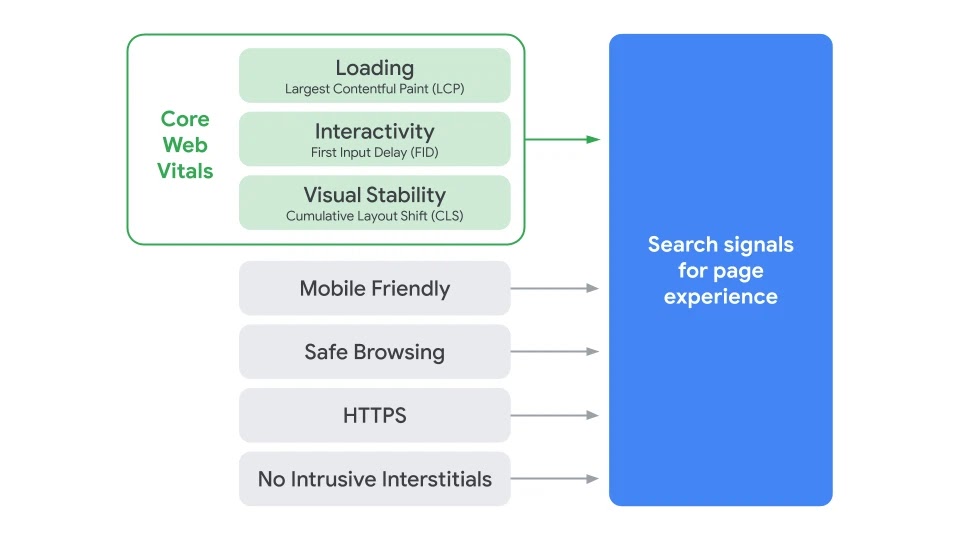
Very recently, a Google research team published a research paper announcing aspirations to implement Knowledge Vault as a search ranking factor. This means that rather than a collection of information simply being shown to users alongside search results – as with Knowledge Graph – the Vault would control all the information on the search results page. Sites that contain information Google considers true would be ranked highly, and sites that contain dubious information would be penalised.
Whilst this is a suggestion still only in its formative period, it’s one that would entirely alter the way Google search works.
At the moment, sites are ranked according to a number of factors, one of these being links. The more links a site has from trustworthy sources, the more trustworthy that site is considered. This is a largely human process; when you link to a site, you’re showing a vote of confidence.
However, a ranking based on the Knowledge Vault would take away this human influence. As the Vault is an autonomous system, it and it alone decides what separates fact from truth, and what makes a site trustworthy.
Current ranking factors like links are far from perfect; something testified by algorithms like Penguin designed to halt manipulative link-building. However, possibilities for manipulating the Knowledge Vault in theory still exist. If the Vault is simply collecting together information it views as similar, and deciding truthfulness based on this, then what’s to stop webmasters from sprinkling their “facts” across the web in an attempt to manipulate higher rankings? Plus, what about dubious information that large numbers of people on the web consider to be true? Does this mean that moon landing conspiracy theories and folk health remedies should be considered facts, and afforded a high ranking? What about “facts” that are opinion based? Should the statement “Noel Edmond’s best days are behind him” be deemed any more truthful than “Noel Edmonds has a long and fruitful future ahead in show business”?
Perhaps more importantly, the implementation of a Knowledge Vault based ranking system is a step towards Google controlling a large flow of information. Whereas with the current ranking system, if a piece of dubious information is encountered, this can be argued against; a healthy discussion can be formed. However, with the implementation of this algorithm, there will be no need for discussion; just a nod of the head as Google pumps out a stream of complete, inarguable “facts ”. With this move, Google could be taking the power to invest confidence in information and sites away from users; something surely more important than encountering the odd “spider eats dog” article.
With this being said, and as Google haven’t imposed any real plans for implementation, at this point we can only speculate how a knowledge based search rankings system would work. It may be that Google could simply decide to implement a fact ranking alongside existing systems – perhaps displayed within a search snippet – something which at the time of writing seems a safer and more feasible option. In the unlikely eventuality that a full overhaul does take place, users may even become savvier, and more clued up to whether they’re being shown sketchy information. In any case, it’s not as if Google has never made big changes to the way search works before, and we’ll look forward to watching and adapting to whatever plays out.